Best HydraFacial in Bangalore | Augusté Skin Facial Bangalore
- Home
- About Us
- Services
- Clinical Facials
- soft peels
- Mechanical Facial
- Micro-channeling Therapy
- Advanced Machine
- Bio – stimulators
CLINICAL FACIALS
SOFT PEELS
Mechanical Facial
MICRO-CHANNELING THERAPY
Bio - Stimulators
- Products
- Gallery
- Testimonials
- Blog
- Contact us
Melasma Explained: Causes, Treatments & Natural Prevention Tips
Discover what causes melasma, effective treatments, and natural prevention tips in this complete 2025 skincare guide.

Table of Contents
Melasma is a common but stubborn skin condition that causes brown or greyish patches on the face, usually on the cheeks, forehead, or upper lip. It’s harmless, but it can deeply affect confidence because of its uneven appearance.
This pigmentation happens when skin cells produce too much melanin, often triggered by sun exposure, hormones, or genetics. Since it affects both the surface and deeper layers of the skin, melasma needs more than just one treatment to fade.
Managing melasma takes patience and consistency, but with the right mix of professional treatments, gentle skincare, and sun protection, it can be controlled effectively for clearer, glowing skin.
What Is Melasma?
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes brown or grey-brown patches on the face, especially on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. It happens when pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) create too much melanin, leading to uneven skin tone.
It’s most common in women between 20–50 years old and often linked to hormonal changes, sun exposure, genetics, or birth control use. That’s why it’s sometimes called the “mask of pregnancy.”
Though melasma is harmless, it can be frustrating and affect confidence. Because it’s influenced by multiple factors and tends to recur, consistent care and combination treatments are key to keeping it under control and improving skin clarity over time.
Symptoms of Melasma
Melasma usually appears as dark, flat, and irregular patches on sun-exposed areas of the skin. These patches are painless and non-itchy, but they can cause emotional distress due to their visible appearance.
The most common symptoms and characteristics include:
- Brown or greyish-brown discolouration on the skin
- Flat, even-textured patches (not raised or scaly)
- Symmetrical distribution, often appearing on both sides of the face
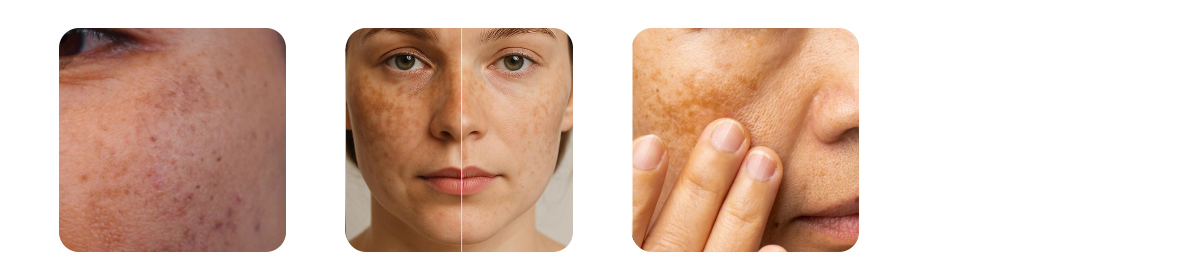
- Commonly affected areas:
- Cheeks
- Forehead
- Bridge of the nose
- Upper lip
- Chin
In some cases, especially those related to excessive sun exposure or severe pigmentation, melasma may also appear on the neck, forearms, or other sun-exposed areas.
While melasma doesn’t cause pain, itching, or irritation, it can have a significant emotional and psychological impact, often affecting self-esteem and leading many to seek cosmetic or dermatological treatments.
Causes of Melasma
Melasma can develop due to a combination of internal and external factors. Understanding these triggers is essential for effective treatment and long-term prevention.
1. Sun Exposure
Sun exposure is the number one cause and the most common trigger of melasma. Ultraviolet (UV) rays stimulate melanocytes (the pigment-producing cells) to create excess melanin, leading to dark patches. Even a few minutes of unprotected sun exposure can worsen existing melasma or cause new pigmentation to appear.
- Prolonged outdoor activities, tanning, or inconsistent sunscreen use can increase risk.
- Melasma often returns after treatment if sun protection isn’t maintained.

2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal imbalance plays a major role in melasma development. Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels can overstimulate melanocytes, causing uneven pigmentation.
- Pregnancy is a common trigger, which is why melasma is often called the “mask of pregnancy” (chloasma).
- Birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy (HRT), menopause, or thyroid imbalances can also contribute to melasma flare-ups.

3. Genetic Predisposition
Genetics influence how your skin responds to hormonal and environmental factors. If melasma runs in your family, you’re more likely to develop it too.
- It’s especially common in individuals with medium to darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick skin types III–V).
- A family history of pigmentation disorders increases the risk and may make melasma more persistent.

4. Heat and Visible Light Exposure
Melasma isn’t only caused by UV rays, heat and visible light also play a part.
- Infrared heat from cooking, saunas, or hot weather can stimulate melanin production.
- Even visible light from screens, indoor lighting, or electronic devices can trigger pigmentation in sensitive individuals.
- This is why broad-spectrum sunscreens that protect against UVA, UVB, and visible light are crucial.

5. Medications and Skincare Products
Certain medications and skincare products can worsen melasma by irritating the skin or making it more sensitive to light.
- Medications such as anti-seizure drugs, hormonal therapies, or phototoxic drugs can increase pigmentation.
- Harsh skincare products, over-exfoliation, or chemical irritants in cosmetics can damage the skin barrier and aggravate melasma.
- Always patch-test new products and avoid those with fragrance or alcohol, which can irritate sensitive skin.

6. Stress and Lifestyle Factors
Emotional stress and lack of proper skincare routines can contribute to melasma flare-ups. Stress hormones like cortisol may affect melanin activity, while inconsistent skincare or skipping sunscreen can make pigmentation harder to control.

What Really Works: Step-by-Step Melasma Treatment Plan (2025 Update)
Hydrafacial combined with chemical peels to start skin prepping
Melasma is one of the most complicated and stubborn skin conditions to treat. It’s not a one-time fix, it requires patience, consistency, and a personalised combination approach guided by a qualified dermatologist.
Dermatologists now recommend a four-step treatment protocol that delivers the best results when customised for your skin type, pigmentation depth, and lifestyle.
Let’s break down what really works for melasma in 2025, step by step.
Step 1: Chemical Peels – The First Line of Treatment
Chemical peels are often the first professional treatment used for melasma. They exfoliate the upper layers of the skin, remove dead cells, and help new, evenly pigmented skin emerge. Peels also allow better absorption of lightening agents used afterwards.
Common Peels Used:
- Glycolic acid peel – boosts cell renewal and fades dark spots
- Lactic acid peel – gentle exfoliation, suitable for sensitive skin
- Mandelic acid peel – mild peel ideal for darker skin tones
- TCA (Trichloroacetic acid) peel – for deeper pigmentation
- Jessner’s peel – a combination peel for stubborn melasma
Benefits of Chemical Peels:
- Gradually lightens brown or grey patches
- Improves overall skin tone and texture
- Stimulates new cell turnover
- Enhances absorption of topical creams
Frequency: Every 3–4 weeks under a dermatologist’s supervision.
Caution: Avoid harsh or DIY peels. Always get peels done by a trained professional to prevent irritation or post-inflammatory pigmentation.
Pro Tip: Use broad-spectrum SPF 50+ sunscreen daily after peels, your skin is more photosensitive post-treatment.
Step 2: Solid Home Care from Your Doctor – The Core of Maintenance
After professional treatments, consistent home care is essential to maintain and enhance results. Melasma can easily recur if home care and sun protection are neglected.
Your dermatologist will design a personalised routine based on your skin type and sensitivity.
Key Components of an Effective Home-Care Routine:
Topical Creams:
- Hydroquinone (2–4%) – gold-standard depigmenting agent
- Kojic acid, Arbutin, Azelaic acid, Niacinamide, or Tranexamic acid – gentler alternatives that inhibit melanin production
- Retinoids (Tretinoin) – promote cell turnover and enhance penetration of lightening creams
- Mild corticosteroids – reduce inflammation (only under medical supervision)
Antioxidant Serums:
- Vitamin C – brightens skin and fights oxidative stress
- Niacinamide – improves skin barrier and reduces redness
Sun Protection:
- SPF 50+ broad-spectrum sunscreen – the single most critical product for melasma patients
- Reapply every 2–3 hours, even indoors or on cloudy days
Moisturisers & Cleansers:
- Use gentle, non-comedogenic, and fragrance-free products to maintain hydration and prevent irritation
Consistency is key. Even after visible improvement, continuing your prescribed routine helps maintain results and prevent relapse.
Avoid: Over-the-counter bleaching creams, harsh scrubs, or alcohol-based toners, they can irritate your skin and worsen pigmentation.
Step 3: Micro-needling – Stimulate Skin Renewal and Enhance Product Absorption
Micro-needling is a minimally invasive procedure that creates controlled micro-injuries in the skin using fine needles. This process stimulates collagen production and enhances the absorption of brightening serums and active ingredients.
How It Works:
Tiny punctures trigger the skin’s natural healing process, promoting regeneration and allowing deeper penetration of treatments like vitamin C, tranexamic acid, or PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma).
Benefits of Micro-needling:
- Improves uneven skin tone and texture
- Boosts collagen and elastin production
- Helps fade deep pigmentation
- Increases effectiveness of topical creams
Treatment Schedule: Every 4–6 weeks under dermatological supervision.
Combination Therapy: Works best when combined with brightening serums, vitamin infusions, or tranexamic acid formulations.
Note: The skin may appear slightly red post-treatment, this is normal and subsides within a day or two.
Step 4: Q-Switch Laser Toning – Advanced Pigment Reduction
Q-Switch Laser Toning (commonly using the Nd: YAG laser) is one of the most advanced and effective tools for treating stubborn melasma that doesn’t respond to topical therapy alone.
How It Works:
The laser emits ultra-short pulses of energy that target and break down melanin clusters deep within the skin without damaging the surface layer. The fragmented pigment is then gradually removed by the body’s natural processes.
Benefits of Q-Switch Laser Toning:
- Reduces deep and surface-level pigmentation
- Evens out skin tone
- Improves clarity and radiance
- Minimal discomfort and downtime
Treatment Plan:
- Usually requires 6–10 sessions, spaced 2–4 weeks apart
- Best results when combined with sunscreen, topical therapy, and maintenance skincare
Important Note:
Laser treatments should only be performed by trained dermatologists. Incorrect settings or overuse can lead to post-inflammatory pigmentation or worsen melasma.
Prevention Tips for Melasma
Preventing melasma from coming back or getting worse takes consistent care and smart habits. It’s not curable, but with protection and patience, you can keep it under control.
1. Wear Sunscreen Every Day
Your best defense is daily sunscreen!
Use a broad-spectrum SPF 50+ even indoors, UV and visible light can still reach you. Reapply every 3–4 hours when outside.
Choose mineral or tinted sunscreens with zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, or iron oxide for full protection.

2. Stay Sun-Safe with Protective Gear
Add a physical shield, wear a wide-brimmed hat, sunglasses, and scarves.
Avoid the sun between 10 AM and 4 PM, and remember, even cloudy days count!

3. Avoid Heat & Harsh Products
Heat can trigger melasma. Skip saunas, hot yoga, and steam rooms.
Avoid harsh scrubs, alcohol-based toners, or DIY remedies like lemon juice.
Also, avoid waxing on melasma-prone areas, it can irritate the skin.

4. Keep a Gentle Skincare Routine
Gentle and consistent wins the race.
Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers. Stick to simple, steady routines and avoid over-exfoliating or frequently switching products.
Follow your dermatologist’s plan regularly.

5. Eat Skin-Healthy Foods
A nutritious, antioxidant-rich diet supports clearer skin.
Add fruits, greens, nuts, seeds, and green tea.
Stay hydrated and cut down on sugar, alcohol, and processed foods.
Vitamins C and E help repair and protect skin naturally.

6. Visit Your Dermatologist Regularly
Melasma needs ongoing care.
Schedule check-ups every few months to adjust treatments if needed.
Maintenance options like chemical peels, laser toning, or microneedling can help keep results steady.

How Long Does Melasma Treatment Take?
Melasma treatment is a gradual process that requires consistency, patience, and professional care. Most people begin to notice visible improvement after 6 to 12 weeks of regular treatment. However, complete fading often takes year, depending on the severity of pigmentation, skin type, and treatment methods used.
It’s important to understand that melasma is one of the most complex pigmentation disorders to treat. It doesn’t clear overnight, and results vary from person to person. The key lies in commitment and persistence, following a proper skincare routine, using prescribed treatments, and protecting your skin from sun exposure daily.
A combination of chemical peels, topical creams, micro-needling, and Q-Switch laser toning can help achieve brighter, more even, and glowing skin over time. Even after significant improvement, maintenance therapy is crucial to prevent recurrence.
Since melasma can easily return, especially if sunscreen is skipped or hormonal triggers persist, regular dermatologist follow-ups are essential to keep the condition under control and ensure long-term results.
In short:
👉 Visible results in 6–12 weeks
👉 Major improvement in 3–6 months
👉 Ongoing care needed for long-term control
Consistency is your best ally, with proper medical guidance and daily sun protection, melasma can be effectively managed and significantly improved.
Can Melasma Be Cured Permanently?
Unfortunately, there is no permanent cure for melasma yet. Melasma is a chronic skin condition influenced by several internal and external factors such as hormonal changes, sun exposure, and genetics. While it cannot be completely cured, it can be effectively managed and lightened with the right treatment plan and consistent care.
Advanced combination treatments, such as the 4-step approach involving chemical peels, dermatologist-prescribed home care, microneedling, and Q-Switch laser toning, can dramatically fade pigmentation and keep it under control for years. With proper maintenance and medical supervision, many people achieve clear, even-toned skin and long-lasting improvement.
The key to success lies in long-term management:
- Protect your skin daily with a broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 50+).
- Follow your dermatologist’s prescribed skincare routine consistently.
- Avoid triggers like sun exposure, heat, and hormonal fluctuations whenever possible.
In short, while melasma cannot be cured completely, it can be controlled effectively and kept from recurring with dedicated care and preventive maintenance.
Final Thoughts
Melasma may be one of the most complicated skin conditions to treat, but it’s not impossible to manage. With the right combination of treatments, including chemical peels, dermatologist-guided home care, micro-needling, and Q-Switch laser toning, real and lasting improvement is absolutely possible.
The secret lies in consistency, patience, and expert supervision. Melasma treatment is a journey, not a quick fix, and every small improvement brings you closer to clearer, brighter, and more even-toned skin.
Strict sun protection, regular follow-ups, and a personalised skincare routine are the cornerstones of success. When followed diligently, these steps can transform your skin, helping you regain a radiant, confident glow, not through overnight miracles, but through dedication and the right care.
FAQs on Melasma (2025 Edition)
The primary causes of melasma are hormonal changes (like pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone therapy) and sun exposure. UV rays stimulate melanin production, worsening pigmentation. Genetics can also increase your risk.
Sometimes, melasma caused by pregnancy or temporary hormonal changes may fade once hormones stabilise. However, in most cases, it requires professional treatment to fade significantly and stay under control.
Yes, when performed by an experienced dermatologist. Q-Switch Laser Toning is one of the safest and most effective methods for targeting deep pigmentation without harming the skin surface.
You can maintain results with dermatologist-prescribed creams like hydroquinone, kojic acid, azelaic acid, or vitamin C serums. However, professional treatments such as chemical peels, micro-needling, and laser toning are often necessary for deeper pigmentation.
Avoid direct sun exposure, harsh exfoliants, alcohol-based toners, and unprescribed bleaching creams. Always use gentle skincare and reapply sunscreen every 2–3 hours when outdoors.
Yes. Stress can worsen melasma by disrupting hormones, while a diet rich in antioxidants, like vitamin C, E, green tea, and leafy greens, supports skin healing and helps control pigmentation.